INTRODUCTION:
A pick-and-place robot car is a versatile robotic platform that seamlessly integrates mobility with precision object manipulation. This project involves a Bluetooth-controlled, four-wheeled robotic vehicle equipped with a servo-driven robotic arm or gripper. Designed to navigate to a target location, the robot uses its arm to grasp objects, transport them, and accurately place them at predefined destinations. The system is operated via an Android app, enabling users to wirelessly control movement, arm positioning, and gripping actions. Ideal for industrial automation, warehouse logistics, or robotics competitions, this project demonstrates practical applications of mechatronics, wireless communication, and real-time control systems. Below, we break down its core components and explain how they interact to achieve these tasks.
Working Principle
The pick-and-place robot car operates based on the following principles:
Mobility: The robot car moves to the target location where the object is to be picked up. This movement is controlled by a set of wheels driven by DC motors.
Sensing: Sensors such as ultrasonic sensors are used to detect the presence of obstacles and navigate the robot car to the target location.
Object Detection and Positioning: Once at the target location, the robot uses additional sensors or cameras to locate and position itself relative to the object to be picked up.
Pick Mechanism: A robotic arm or gripper, controlled by servos or stepper motors, is used to pick up the object.
Placement: The robot car then moves to the designated drop-off location, where the robotic arm or gripper places the object.
Components Description
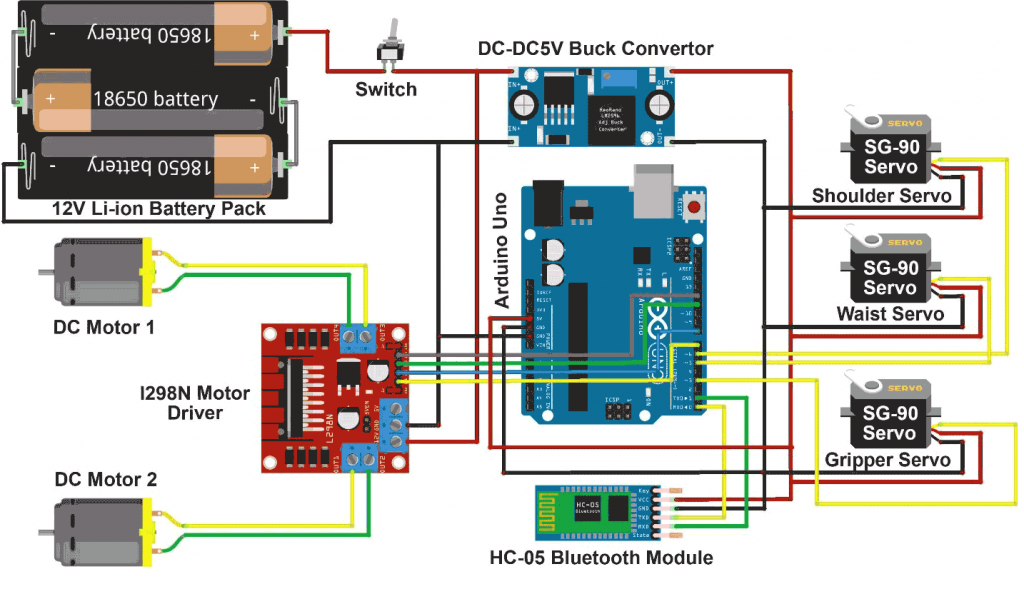
1. Arduino Board
Description: The central microcontroller that processes sensor data and controls the motors and servos.
Function: Manages the overall operation of the robot car, including movement, object detection, and manipulation.
2. DC Motors and Motor Driver (e.g., L298N)
Description: DC motors drive the wheels of the robot car, and the motor driver controls the motors.
Function: Provide mobility to the robot car.
3. Servo Motors
Description: Used to control the movements of the robotic arm or gripper.
Function: Allow precise control of the arm for picking and placing objects.
4. Robotic Arm/Gripper
Description: The end effector that physically picks up and places objects.
Function: Manipulates objects as required by the task.
5. Ultrasonic Sensors (e.g., HC-SR04)
Description: Sensors that measure distance to detect obstacles and help navigate the robot car.
Function: Provide input to avoid collisions and ensure the robot reaches the correct location.
6. Infrared Sensors or Camera (Optional)
Description: Used for more precise object detection and positioning.
Function: Assist in accurately locating the object to be picked up.
7. Power Supply (Battery Pack)
Description: Provides the necessary voltage and current to power the motors, servos, and Arduino.
Function: Ensures the robot car has sufficient power to operate.
8. Chassis
Description: The physical frame of the robot car, which holds all the components together.
Function: Provides structural support and housing for all components.
Project Working Steps:
Initialization:
Power up the system and initialize all components. This includes setting up the Arduino, sensors, motors, and servos.
Movement to Target Location:
Use ultrasonic sensors to navigate the robot car to the location of the object. The Arduino processes the sensor data to avoid obstacles and guide the car.
Object Detection and Positioning:
Once at the target location, use additional sensors (like infrared or a camera) to precisely locate the object. Adjust the car’s position if necessary.
Pick Operation:
Control the robotic arm or gripper using servo motors to pick up the object. This involves precise movements of the arm to grip the object securely.
Transport:
After picking up the object, navigate the robot car to the drop-off location using the same obstacle avoidance and navigation techniques.
Place Operation:
Control the robotic arm or gripper to place the object at the designated location. Ensure the object is released securely.
Return to Start or Idle State:
After placing the object, the robot car can either return to its starting position or enter an idle state awaiting further instructions.